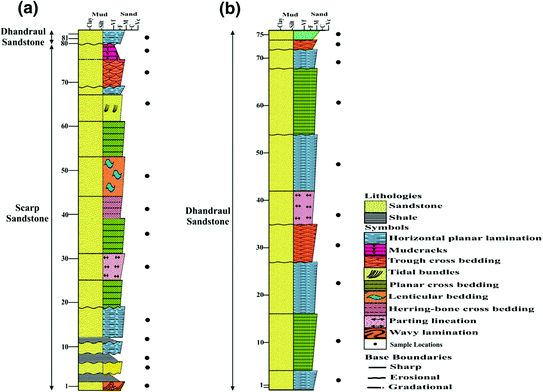
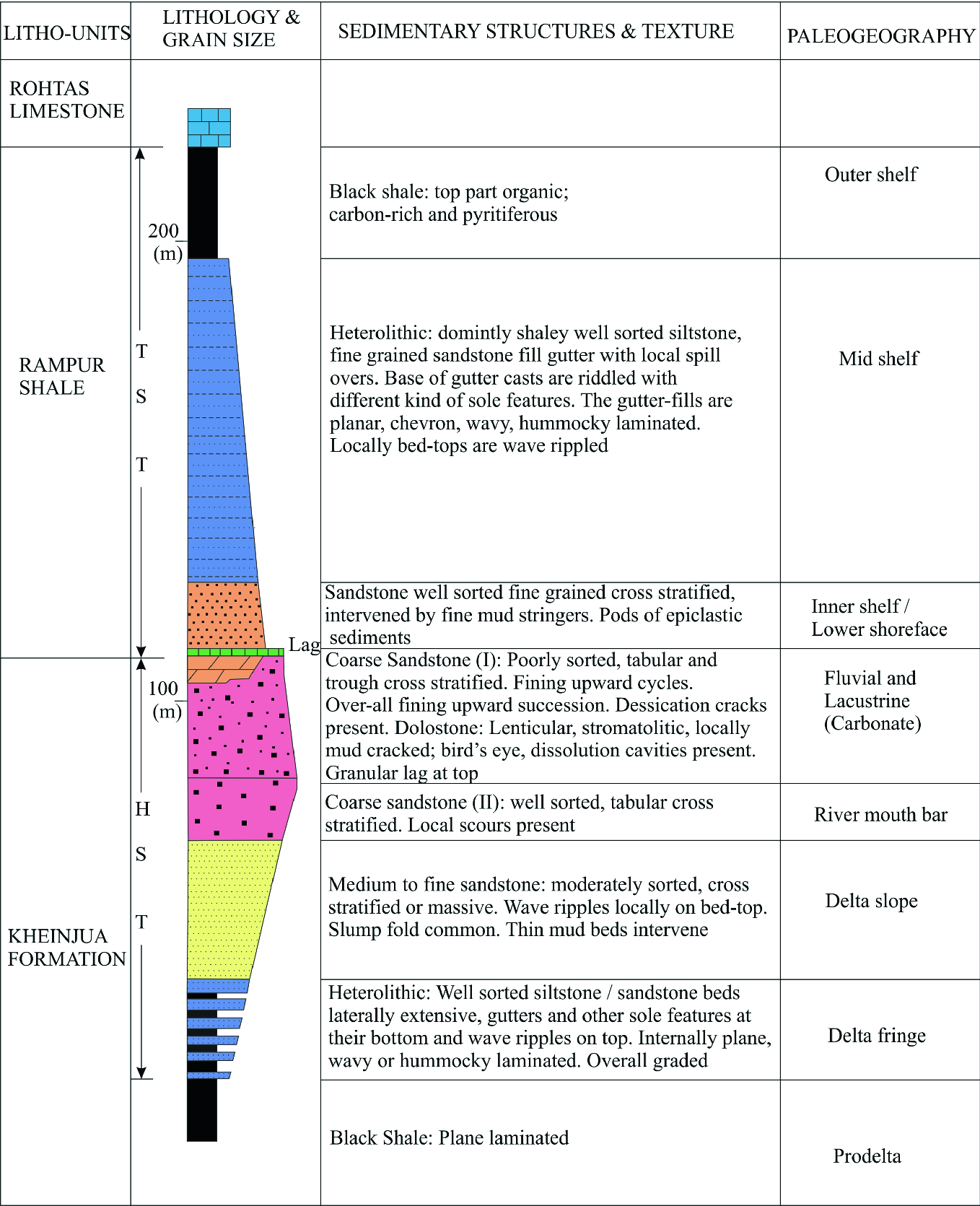
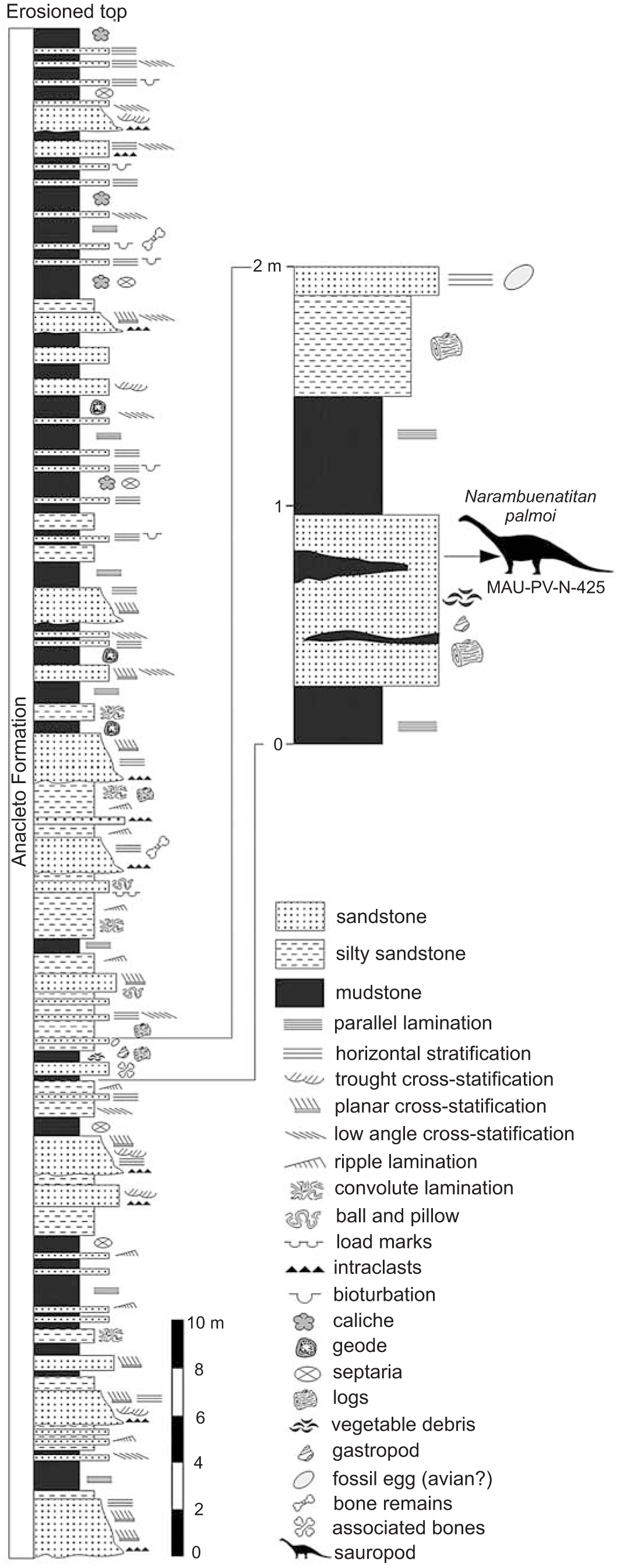
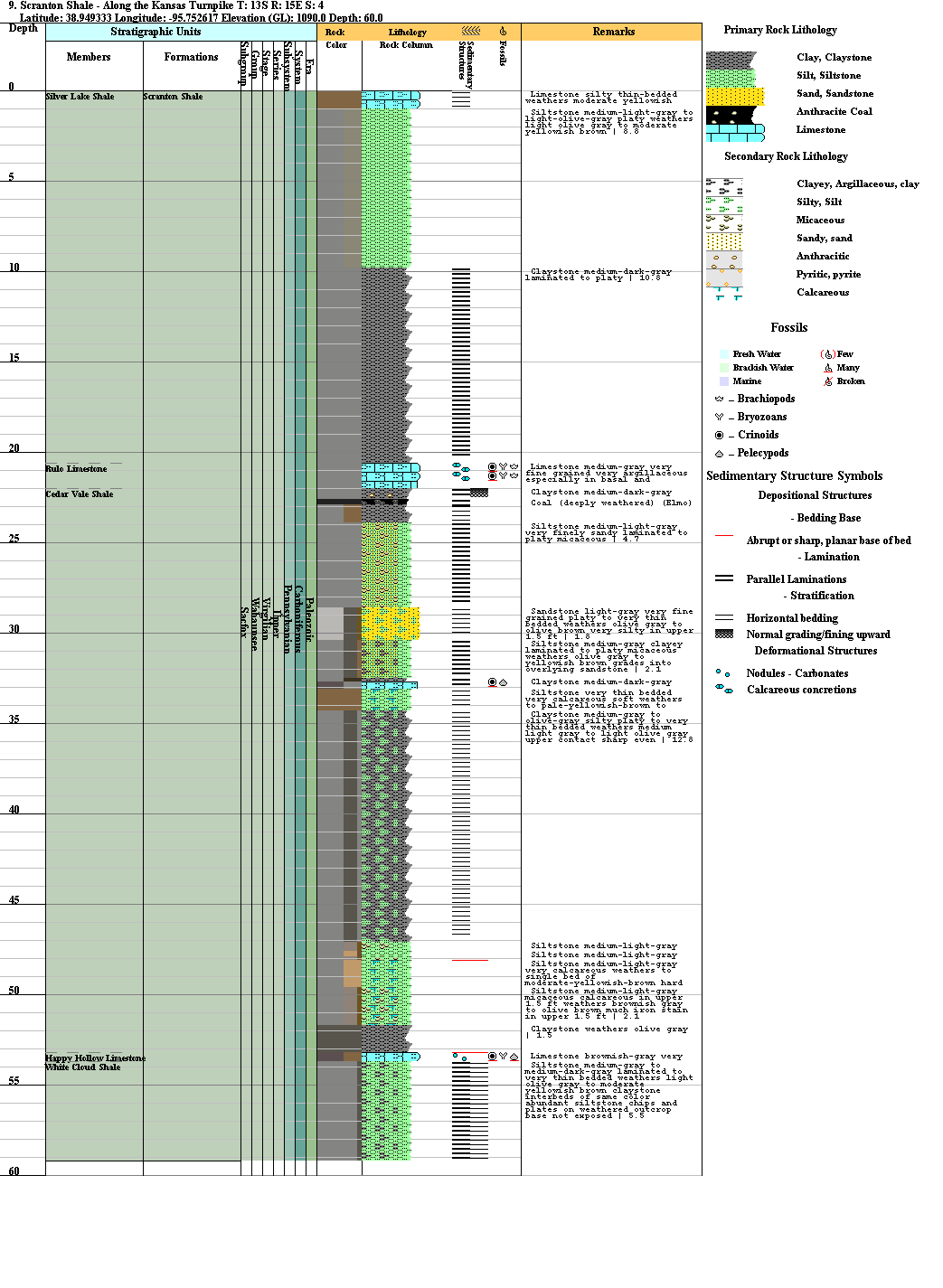
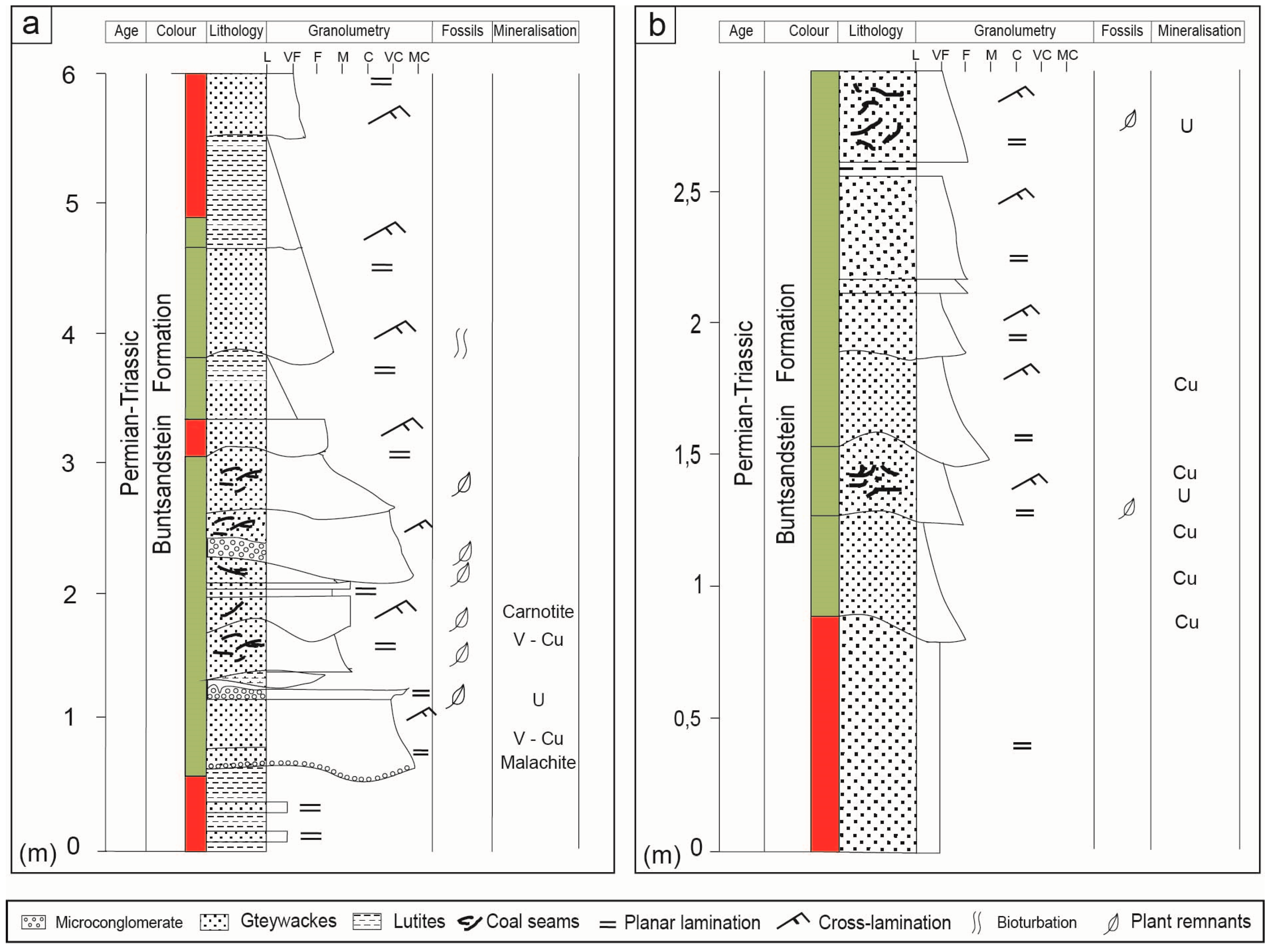
Planar Lamination On Stratigraphic Column
If you hypothesized that set of a fining upward sandstones were turbidites which have planar lamination and current ripple cross lamination but there is also trough cross stratification in a number of the beds ask yourself if there is a way for trough cross stratification to form in turbidites.
Planar lamination on stratigraphic column. The late jurassic stratigraphic column of saudi arabia. Here are some example stratigraphic columns to think about. Here palaeocurrent indicators are south south eastward mean resultant azimuth 145. Planar lamination step 4.
Divide different units according to the lithology. Which displays a faint planar lamination disrupted by polygonal fractures. Wave action intensely affects lower shoreface only during storm events. Primarily finer sands with layers of mud.
Planar lamination and large scale trough cross stratification are abundant. In addition to the mega ripples planar lamination low angle lamination 4 8 and hummocky cross stratification within the beds are also present. Recognize characteristic sedimentary structures in each unit. Generalized stratigraphic column of the husky creek fm.
Steps when drawing a stratigraphic column photo by huan cui 1. Evaluate how the vertical sequence of sedimentary structures changes to refine or correct your environmental interpretations. Through transect of exposed strata along the coppermine river. Thin lenses and stringers of igneous pebble conglomerate occur near the base of the unit.
The planar laminated to low angle cross stratified facies typically shows fine lamination that is geometrically arranged in bed sets having horizontal to low angle cross stratification. Estimate the thickness of the unit. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. Look for sedimentary structures that are characteristic of a specific environment or process.
Use appropriate symbols when drawing the stratigraphic column. Posted by dawn sumner at 10 24 am. Turbidites vs river channel deposits. Interpreting stratigraphic columns step 1.
Planar lamination or stratification. In geology cross bedding also known as cross stratification is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. Mud rip up clasts detrital peloids and petrified woody debris are common. Stratigraphic age is based on gradstein et al s 2012 time scale.
Cross stratification angles vary from 0 to 20 fig.